Garlic is a versatile and flavorful ingredient that is a staple in many cuisines around the world.
Not only does it add a delicious flavor to meals, but it also has numerous health benefits, making it a valuable addition to any garden. Growing garlic is relatively easy and can be done in any size garden or even in containers.
Let’s look at everything you need to know to successfully grow garlic and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
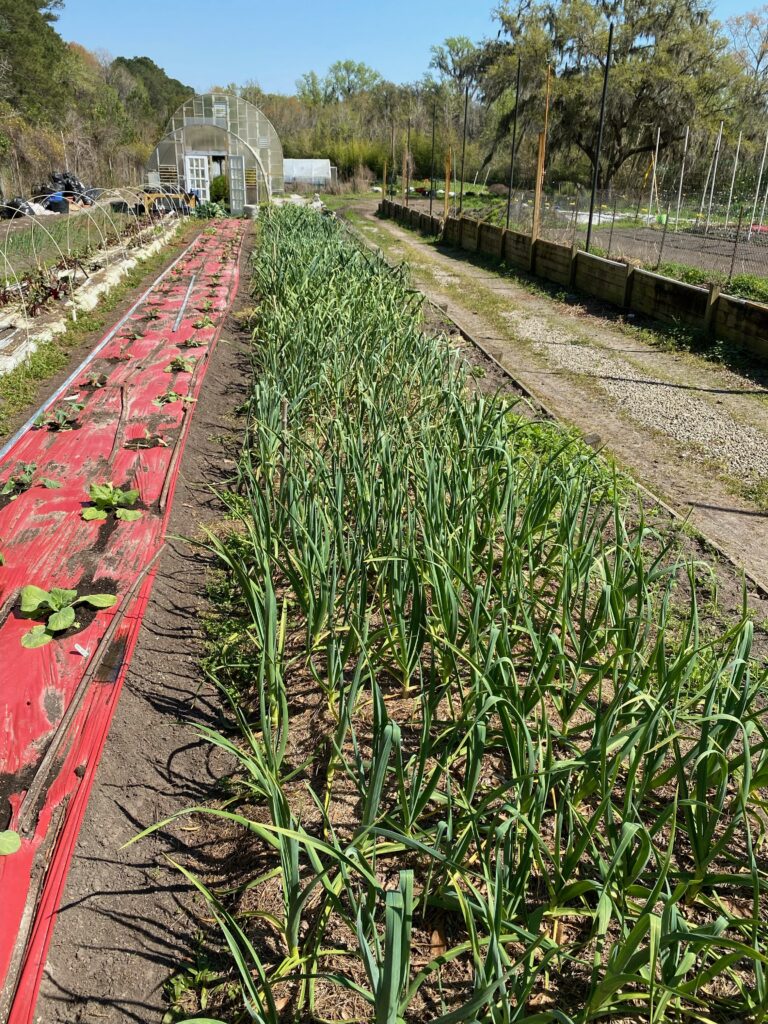

Types of Garlic
It’s a good idea to try many different types of garlic because each variety has its own unique flavor and characteristics, which can add depth and complexity to your dishes. Garlic can vary in flavor from mild and sweet to spicy and pungent, and trying different types can help you discover new flavors and enhance your culinary repertoire.
Garlic can originate from many different parts of the world, including Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. Each region has its own garlic varieties that have been cultivated for centuries, and exploring these varieties can be a fun and educational way to learn about different cultures and cuisines.
Whether you grow your own garlic or seek out different varieties at your local market, trying different types of garlic can be a delicious and rewarding culinary adventure. Here is a list of top 5 types of garlic that you can consider planting.
Rocambole Garlic – This is a popular garlic variety that has a rich, complex flavor with a hint of sweetness. It has a papery skin and a curly scape.
Porcelain Garlic – This variety has a mild, creamy flavor and is known for its large cloves. It has a thick, hardy skin that makes it great for storage.
Purple Stripe Garlic – This garlic has a rich, spicy flavor and a beautiful purple-striped skin. It’s often used in traditional Eastern European dishes.
Artichoke Garlic – This is a softneck garlic variety that is easy to grow and has a mild, sweet flavor. It has a tight, layered skin and can be braided for easy storage.
Elephant Garlic – While not technically garlic, elephant garlic is a member of the Allium family and has a mild, garlic-like flavor. It has large cloves and a thick, papery skin.
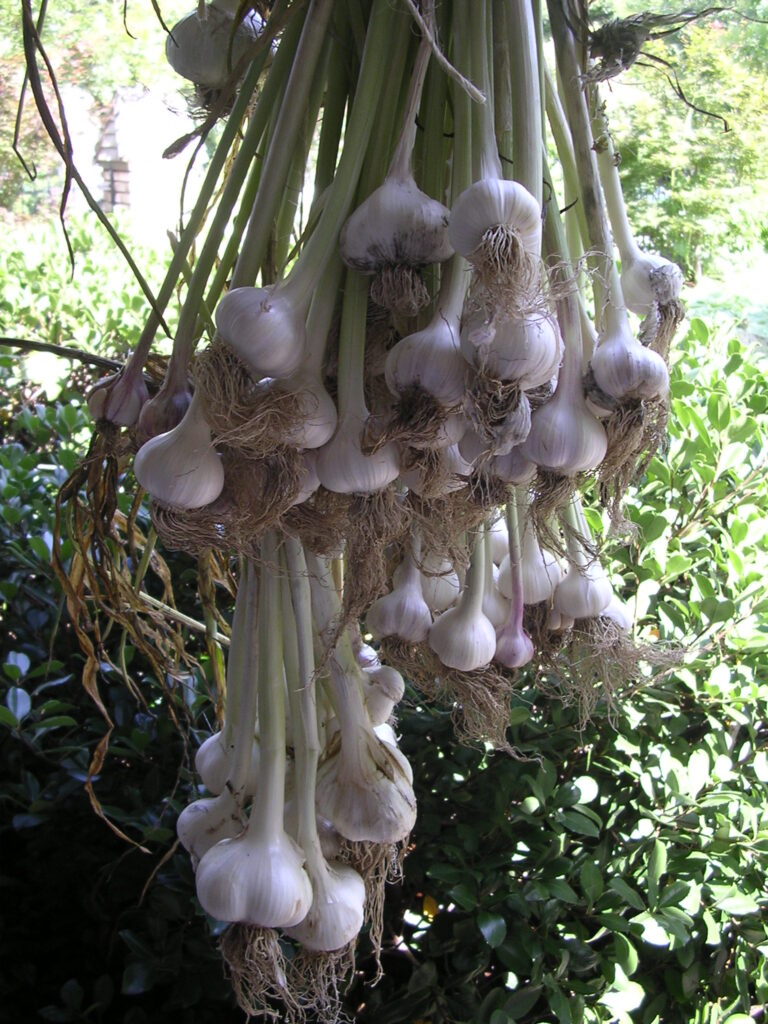

Softneck vs. Hardneck Garlic
Softneck garlic, also known as artichoke garlic, is the most common type of garlic found in grocery stores. It has a soft stem that can be braided, making it easy to store. Softneck garlic typically has a milder flavor and smaller cloves than hardneck garlic. It also tends to produce more cloves per bulb, making it a popular choice for commercial growers.
Hardneck garlic, also known as stiffneck garlic, has a stiff stem that cannot be braided. It produces a scape, or flower stalk, which needs to be removed in order to encourage bulb growth. Hardneck garlic typically has a stronger, more complex flavor than softneck garlic, and larger cloves with easier-to-peel skin. It also tends to be more cold-hardy and better suited for colder climates.
How to Plant and Harvest Garlic
Planting and harvesting garlic is relatively easy, making it a great choice for both experienced and novice gardeners.
Garlic is typically planted in the fall and requires little maintenance throughout the winter months. Once the weather warms up in the spring, garlic will start to grow and will be ready to harvest in mid-summer. Harvesting garlic is a simple process that involves loosening the soil around the bulbs and pulling them out of the ground.
After harvesting, garlic needs to be dried for a few weeks before it can be stored. Overall, planting and harvesting garlic requires minimal effort and can be a great way to enjoy a bountiful harvest of flavorful and nutritious garlic.

Garlic Soil Preparation
Garlic prefers soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Soil pH is important for garlic because it affects the availability of nutrients in the soil, and pH levels that are too high or too low can limit the growth and development of the garlic plants.
If the soil pH is too low, adding lime can help raise it. If the pH is too high, adding sulfur can help lower it. Testing the pH of your soil before planting garlic can help ensure that your plants have the optimal conditions for growth and can lead to a more successful harvest.
Planting Garlic
Garlic is typically planted in the fall, about 4-6 weeks before the ground freezes. This allows the garlic to establish roots before winter and start growing as soon as the soil thaws in the spring. To plant garlic, start by selecting a sunny location with well-draining soil. Before planting, prepare the soil by adding compost or well-rotted manure to improve its fertility and structure. Next, break apart the bulbs into individual cloves, making sure to leave the papery skin intact.
Plant the cloves pointed end up, about 2 inches deep and 6 inches apart, and cover with soil. Water the soil well and cover with a layer of mulch, such as straw or leaves, to protect the garlic from frost and weeds.

How to Harvest Garlic
Garlic is typically ready to harvest in mid-summer, once the leaves start to turn yellow and die back. Harvesting garlic is a simple process that can be done in five easy steps.
First, about two weeks before harvest, stop watering the garlic to allow the bulbs to dry out. Next, use a garden fork to gently loosen the soil around the garlic bulbs. Carefully pull the garlic bulbs from the soil, being careful not to damage them. Once harvested, allow the garlic to dry in a warm, well-ventilated spot for 2-3 weeks.
Finally, once the garlic is dry, remove the papery skin and store it in a cool, dry spot. Garlic can be braided or stored in mesh bags for easy storage. Following these steps will help ensure that you have a bountiful harvest of delicious and nutritious garlic.
Tips for Mitigating Pests and Diseases
Like all plants, garlic can be susceptible to pests and diseases. Here are some tips to help mitigate these issues:
Plant disease-resistant varieties – Choose garlic varieties that are known to be resistant to common diseases like white rot and rust.
Rotate crops – Avoid planting garlic in the same spot year after year, as this can lead to a buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
Use companion planting – Planting garlic using the companion planting method can help deter pests and improve soil health. Plant garlic alongside other plants like chives, onions, and herbs.
Mulch – Mulching around the garlic plants can help keep the soil moist and cool, while also suppressing weeds that can harbor pests.
Practice good hygiene – Clean up any debris or dead plant material around the garlic plants to help prevent the spread of diseases.
Use organic gardening methods – Consider using natural methods to control pests, such as introducing beneficial insects or using insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Inspect regularly – Regularly inspect your garlic plants for signs of pests or diseases, so you can catch any issues early and take action before they spread.

Growing Garlic Conclusion
Growing garlic is a rewarding and easy way to add flavor and nutrition to your meals while also enhancing the beauty of your garden.
With our tips and tricks for growing garlic, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of flavorful garlic while mitigating the risks of pests and diseases. So why not try growing garlic in your garden this season and experience the satisfaction of growing your own delicious and healthy food?
Also, if you want to start planning your garden for garlic, try our garden planner Hortisketch.